Ethylene Valence Electrons
How many valence electrons do the two carbon atoms in the molecule share with each other in the double bond. Because each carbon is surrounded by three electron.
Structure And Bonding In Ethene The Pi Bond Chemistry Libretexts
It is shown that fragmentation of the molecule occurs as a result of multiphoton ionization of inner-valence electrons.

Ethylene valence electrons. Using linearly polarized 200 fs Tisapphire laser pulses the multiphoton ionization and fragmentation of ethylene was studied. The explanation of the structure of ethylene molecule using the molecular orbital theory The excitation process takes place for the two carbon atoms by acquiring the required amount of energy After the two carbon atoms have been excited the three orbitals of 2s 2p x and 2p y are hybridized forming three hybridized orbitals each of them is named sp² and contains one single electron. Inclusion of electron correlation and relaxation did not have a large effect on the shapes of the valence orbital momentum profiles even though as is the case for ethylene significant improvements were found in the total energies in both cases.
Explain how the VSEPR model Section 310 predicts a bond angle of 1095circ about each carbon in ethane but an angle of 120circ about each carbon in ethylene. The latter VB structures have cumulated weights of 1826 and stabilize the V state by about 09 eV. This decreases the energy of the molecule and increases its stability that determines the geometry of the molecule.
Furthermore a theoretical method of calculating electron momentum distributions for polyatomic molecules has been developed with. The outermost shell is known as the valence shell and the electrons present in that shell are known as valence electrons. All elements have valence shell electrons which are involved in single double or triple bond formation or they remain non-bonded.
We report an electron momentum spectroscopy study of vibrational effects on the electron momentum distributions for the outer valence orbitals of ethylene C 2 H 4. That involve the electronic ground and excited states of the precursor ethylene dication and explore the strong influence of the conical intersections between the different electronic states. The transition metal formally attains the electron configuration of the subsequent noble gas in the periodic table.
Ethylene CHA Number Of Valence Electrons For Each Hydrogen Electron Dot Diagram For Each Element Show How Atoms Arrange To Pair Up Electrons Draw Lewis Structure For The Compound For Each Carbon Total Valence Electrons. The fourth electron is in the p orbital that will form the pi bond. The bond order for ethene is simply the.
Both types of valence bond calculations show that the V state of ethylene is not fully ionic as usually assumed but involving also a symmetry-adapted combination of VB structures each with asymmetric covalent π bonds. The electrons create a negative charge cloud around them. A model is proposed which is able to satisfactorily predict the abundance of the different fragments C 2 H 4 C 2 H 3 and C 2 H 2 as a function of laser intensity.
Ethylene commonly knows as ethene CH 2 CH 2 is the simplest molecule which contains a carbon carbon double bond. Furthermore a theoretical method of calculating electron momentum distributions for polyatomic molecules has been developed with. The Structure of Ethene Ethylene.
If we see the last group we can find out that all the elements are inert gases having eight electrons in their valence. The Lewis structure of ethylene indicates that there are one carbon-carbon double bond and four carbon-hydrogen single bonds. The nondissociative ionization yield is small in ethylene and high in acetylene when compared with the dissociative ionization channels.
We report an electron momentum spectroscopy study of vibrational effects on the electron momentum distributions for the outer valence orbitals of ethylene C2H4. The Lewis structure for ethylene C2H4 is shown. According to VSEPR model the electrons surrounding an atom spread in such a way to minimize repulsion among them.
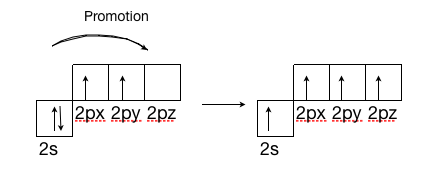
The symmetric noncoplanar e2e experiment has been conducted at an impact energy of 12 keV. All calculations include the angular resolution. In ethene each hydrogen atom has one unpaired electron and each carbon is sp 2 hybridized with one electron each sp 2 orbital.
According to valence bond theory two atoms form a covalent bond through the overlap of individual half-filled valence atomic orbitals each containing one unpaired electron. Experimentally the four carbon-hydrogen bonds in the ethylene molecule have been shown to be identical. The number of valence electrons of an atom is equivalent to its valency which in turn determines the combining capacity of the given atom.
The 18 valence electron 18VE rule introduced in 1927 by Sidgwick is based on the valence bond VB formalism of localized metal-ligand bonds. Electron Dot Diagram For Each Element Show How Atoms Arrange To Pair Up. Sp2 Hybridization The carbon atoms of many of the molecules that we have considered so far have used their four valence electrons to form four single covalent sigma bonds to four other atoms.
18VE rule aka inert-gas rule effective atomic number EAN rule. Have a look at the periodic table. Nitrogen KN Number Of Valence Electrons For Each Nitrogen.
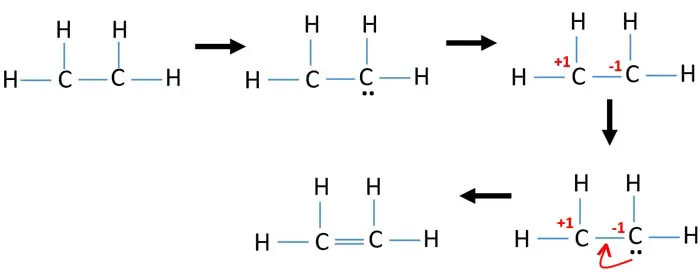
The symmetric noncoplanar e2e experiment has been conducted at an impact energy of 12 keV. Decay are different from those following valence PDI and if electron-electron correlation or entanglement plays a role. Now both carbon has satisfied their octet and four hydrogens have satisfied their duetThis is the CH2CH2 etheneLewis structure.
It is further shown that these latter VB structures rather than the. Look both carbon atoms have 6 valence electrons hereTo have the octetwe need to place two valence electrons between them. Each carbon atom in ethane and in ethylene is surrounded by eight valence electrons and has four bonds to it.
Note how- ever that there are large improvements in the calcu- lated total energy and quadrupole moment of ethy- lene. Ethylene is a centrosymmetric molecule with a CC double bond and therefore the K-shell ionization will not directly allow for observing effects based on core-hole localization. Problem 8 Easy Difficulty.
Ethene C2h4 Lewis Structure Hybridization

C2h4 Lewis Structure Molecular Geometry Hybridization And Mo Diagram Techiescientist

Lewis Dot Structures Cont Chemical Bond Chemistry Notes 11th Chemistry

Ethylene American Chemical Society Chemical Chemistry Society

Explain The Formation And Structure Of Ethylene C2 H4 By Sp2 Hybridization Qs Study
A Hybridised Atomic Orbitals And Chemical Bonding In An Ethylene C 2 Download Scientific Diagram

Structure And Bonding In Ethene The Pi Bond Chemistry Libretexts

A Sigma Single Bond Hybridization For Ethylene B Pi Single Download Scientific Diagram
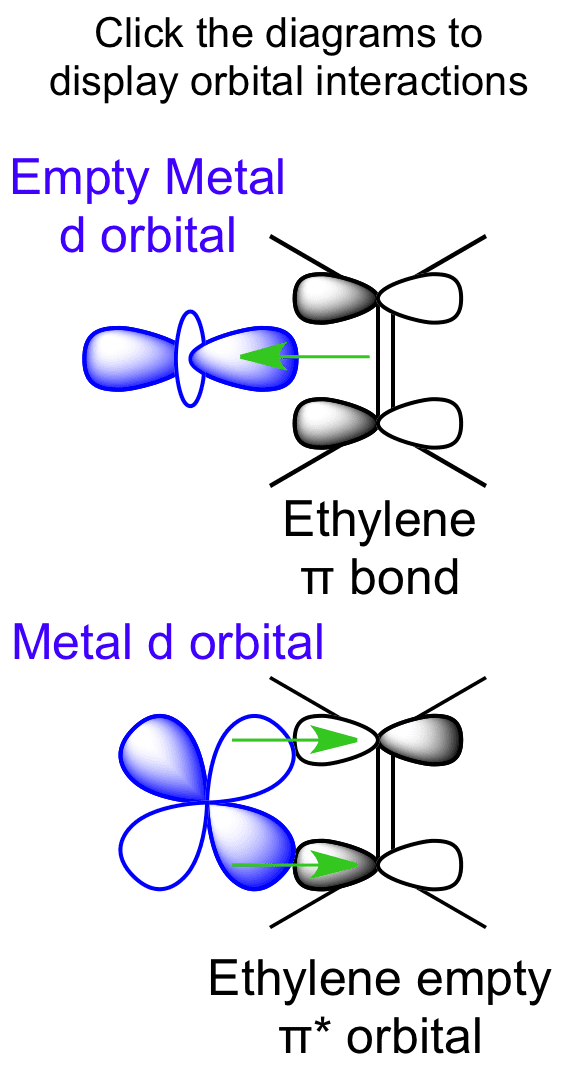
Interactions Between Ethylene Molecular Orbitals And Metal D Orbitals

Orbital Hybridization Organic Chemistry Teaching Chemistry Chemistry Classroom

Bond Angles And The Shapes Of Molecules Chemistry Organic Chemistry Molecules

An Ethylene Signal Transduction Pathway Ethylene Permeates The Membrane And Binds To A Receptor Signal Transduction Chemical Structure Medical School Studying

Ethylene Mos By Lcao 2 4 Youtube

Correlation Diagram For The Maximum Symmetry Approach Of Two Ethylene Download Scientific Diagram

Lewis Structure Ethylene Chemical Bond Diagram Resonance Cao Angle Text Png Pngegg

C2h4 Lewis Structure Molecular Geometry Hybridization And Mo Diagram Techiescientist

Ethene Reactions Of Ethene Properties Of Ethene Chemistry Education Teaching Chemistry Chemistry Help

A Sigma Single Bond Hybridization For Ethylene B Pi Single Download Scientific Diagram

Hybrid Orbitals In Ethyne Organic Chemistry Science Chemistry Teaching Chemistry